When done right, customer marketing builds loyalty and advocacy, driving long-term success for your business. But how can you tell if you're actually making an impact?
That’s where OKRs (objectives and key results) and KPIs (key performance indicators) come in.
These acronymic aids help you cut through the noise and focus on what matters most – making your customers feel valued, heard, and understood.
In the wise words of Avinash Kaushik, Chief Strategy Officer at Croud:
“If you don’t actually know what you’re trying to achieve, it’s also hard to measure success. Try it, you’ll see what I mean.”
In this guide, we're going to look at:
- Why OKRs and KPIs matter for customer marketers
- What an OKR is
- OKR examples in customer marketing
- What a KPI is
- Examples of customer marketing KPIs
- If customer marketing teams are achieving their KPIs
- Real-life KPI insights from top customer marketers
- The difference between OKRs and KPIs
- How to set effective OKRs and KPIs for your customer marketing team
- Best practices for OKR and KPI reporting
Why OKRs and KPIs matter for customer marketers
Customer marketing can be tricky to measure since it revolves around relationships and experiences rather than just numbers. Without clear goals and metrics, it’s easy to lose sight of what really matters. OKRs and KPIs help you:
- Clarify priorities: Everyone stays on the same page about what success looks like.
- Measure impact: See clearly how your efforts are making a difference.
- Stay focused: Avoid distractions and work towards meaningful results.
- Prove value: Show leadership the impact of customer marketing on retention and growth.
- KPIs and OKRs are both good indicators of success. They provide key information about business processes, are monitored regularly, and are mapped to your program, project, or team.
What is an OKR?
OKRs are a simple but powerful goal-setting framework designed to help teams aim high and track progress. Think of them as your business GPS, guiding you toward ambitious goals with clear checkpoints along the way.
- Objectives: These are big, bold goals that set the direction for your efforts. They should be inspiring and challenging.
- Key results: These are the specific, measurable milestones that tell you if you’re making progress toward your objective.
OKRs focus on the process rather than the end result. John Doerr, the pioneer of the OKR, distilled their essence into a simple formula:
“I will [blank] as measured by [blank].”
An OKR might look like this:
“I will [improve advocate signup processes] as measured by [customer interviews and feedback].”
Most, if not all companies will use these to steer their progress. In customer marketing, they help bring method to the madness. OKRs have become indispensable because they:
- Bridge the gap between strategic vision and daily activities
- Align teams around customer-centric priorities
- Create accountability through clear success metrics
- Enable agile responses to changing customer needs
Example OKRs for customer marketing
Here are some examples of common customer marketing goals we hear being used regularly and broadly speaking, they can be split into four pillars:
Customer advocacy OKRs
Focus on driving customer referrals, reviews, and building a base of vocal advocates.
- Number of new advocate sign-ups
- Increase in referral program participation
- Number of customer testimonials collected
- Growth in positive third-party reviews (e.g., G2, Trustpilot)
- Advocate-to-referral conversion rate
To break this down even further, here are some tried-and-tested OKRs you can put to work tomorrow:
- KR1: Increase customer referrals by 25%.
- KR2: Publish 15 customer success stories by year-end.
- KR3: Launch an ambassador program with 50 active participants.
Customer retention and loyalty OKRs
Retention is the backbone of customer marketing – these OKRs help measure long-term success.
- Net promoter score (NPS) improvement
- Churn reduction percentage
- Increase in customer lifetime value (CLV)
- Expansion revenue from existing customers
- Participation rate in retention campaigns (e.g., newsletters, webinars)
- KR1: Increase retention rate from 80% to 85% by Q3.
- KR2: Launch a personalized loyalty program for the top 500 customers.
- KR3: Reduce churn rate by 5% through targeted engagement campaigns.
- KR4: Achieve a 20% increase in upsell and cross-sell revenue within the fiscal year.
- KR5: Elevate NPS score from 45 to 60 in six months.
Product adoption and engagement OKRs
Encouraging customers to fully leverage your product’s value drives stickiness and satisfaction.
- Increase in monthly active users (MAU)
- Feature adoption rate (e.g., % of users engaging with a specific tool)
- Product training session attendance
- Reduction in support ticket volume for key features
- Time-to-value reduction for new customers
- Key result 1: Achieve a 20% increase in monthly active users for “Feature X” within Q1.
- Key result 2: Boost upsell conversions from Feature X users by 10%.
Customer education and enablement OKRs
Empowering customers through knowledge helps build confidence and long-term retention.
- Number of customers completing training or certifications
- Content engagement metrics (e.g., guide downloads, webinar views)
- Increase in self-service help center usage
- Customer feedback score on educational materials
- Time spent engaging with onboarding content
With this approach, you’ll not only celebrate wins that matter, but you’ll also ensure your customer marketing strategy directly contributes to long-term business success.

Defining your customer marketing goals
When setting your customer marketing objectives, don’t fall into the trap of focusing on "feel-good" metrics like open rates or social shares.
While these numbers might look impressive at first glance, they don’t always reflect the deeper impact you’re striving for—customer retention, loyalty, or growth.
For instance:
If 80% of your customer emails get opened, but only 5% of those readers engage with your content, and even fewer upgrade or refer a friend, is that truly a win? Or just an illusion of success?
Metrics that lack a clear connection to customer lifetime value or advocacy can leave your team answering a lot of awkward “But what’s the ROI?” questions from stakeholders. And let's be real – those conversations are no fun for anyone.
So, how should you approach your customer marketing goals?
Align them with measurable, customer-focused outcomes:
- Increase net promoter score (NPS): Are more customers likely to recommend your product?
- Reduce churn rate: Are your efforts keeping more customers around?
- Boost expansion revenue: Are customers upgrading or adding more seats due to your campaigns?
- Drive customer advocacy: How many new customers come from referrals?

Next steps
Now these desired results have been set out, you and your team will have to prioritize certain actions that’ll help you achieve them. The actions taken may look something like this:
Retention rate actions:
- Implement a customer feedback program to gather insights on pain points and areas for improvement.
- Launch a personalized email marketing campaign targeting at-risk customers with tailored offers and content.
- Enhance the onboarding process to ensure customers are well-acquainted with our product's value.
NPS actions:
- Conduct in-depth NPS surveys to identify specific areas where we can enhance the customer experience.
- Create a customer advocacy program to encourage satisfied customers to refer new clients.
- Provide additional training and resources to our support team to improve customer interactions.
Churn rate actions:
- Analyze the reasons behind customer churn through exit surveys and data analysis.
- Implement a dedicated customer success team to proactively address potential issues and provide personalized support.
- Develop a comprehensive knowledge base and self-service resources to empower customers.
Cross-sell and upsell actions:
- Conduct a comprehensive audit of current product offerings to identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities.
- Train the sales and customer success teams to effectively identify and present these opportunities to customers.
- Develop targeted marketing campaigns to promote complementary products or services to existing customers.
Each of these steps will aim to get you to those key results and consequently achieve your overall goal of increased retention and loyalty.

What is a KPI?
While OKRs help you aim for ambitious goals, KPIs are more about monitoring ongoing performance.
KPI literally stands for “key performance indicator.”
on
KPIs are the data points you track regularly to understand how well you’re doing in specific areas.
- Key: Customer retention is a critical factor for long-term business success and profitability.
- Performance: This KPI measures how well your customer marketing efforts are retaining existing customers over a specific period.
- Indicators: It is indicated by the percentage of customers who continue to do business with your company compared to the total number of customers at the beginning of the period. A high retention rate indicates you have been successful in your customer marketing strategies, while a declining retention rate may signal the need for improvements in this area.

Examples of customer marketing KPIs
Now we've established what KPIs are, let's dive into how you can create KPIs based on the most central pillars of customer marketing.
Activity KPIs
Activity KPIs measure the consistency and volume of your customer marketing efforts over time:
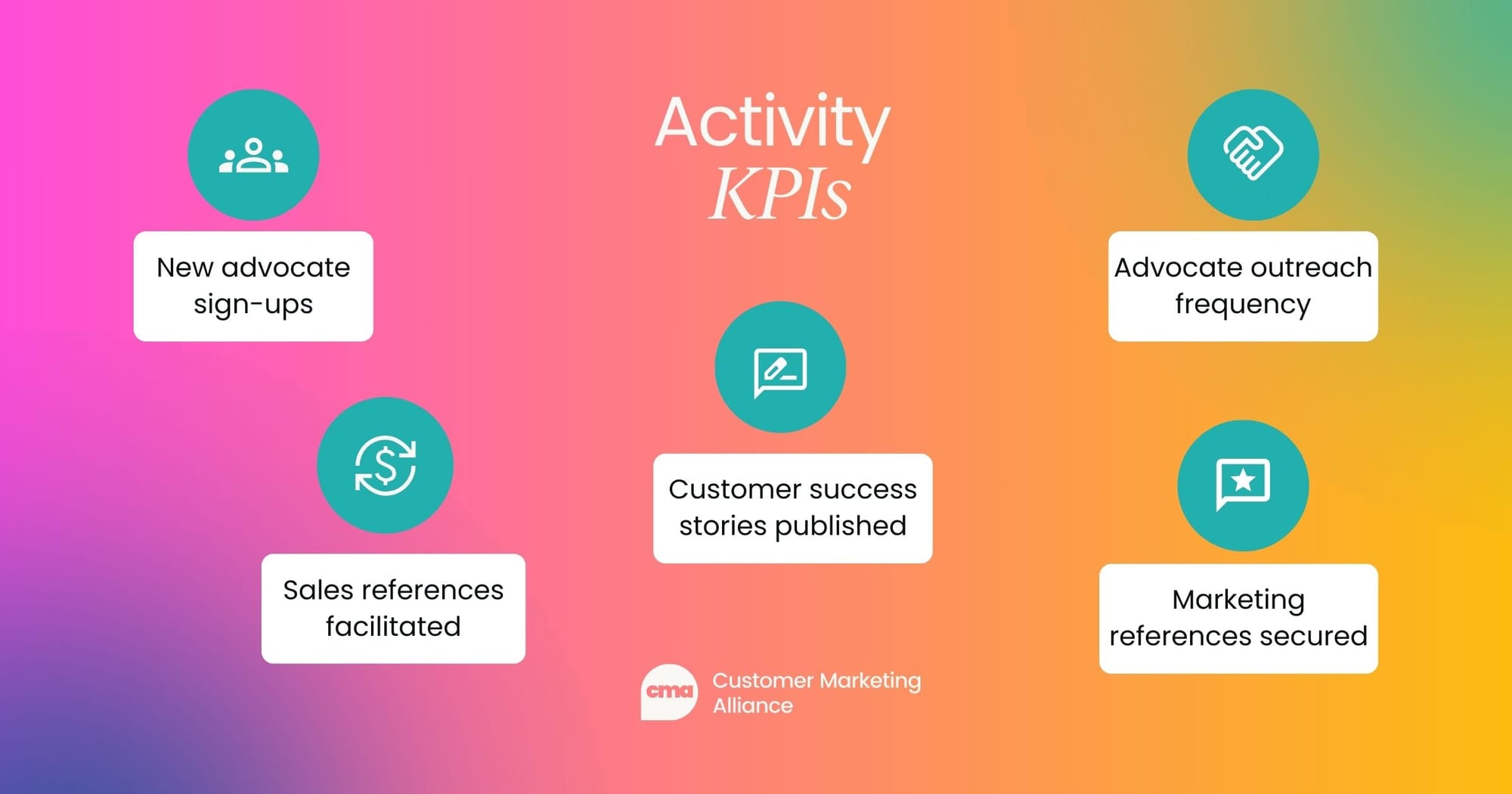
- New advocate sign-ups: Number of new advocates added to your program each month.
- Sales references facilitated: Number of customer references provided for sales enablement during a given period.
- Customer success stories published: Number of case studies, testimonials, or success stories published monthly.
- Advocate outreach frequency: Number of targeted customer campaigns run per month (e.g., newsletters, email campaigns).
- Marketing references secured: Number of customers providing testimonials, video reviews, or public endorsements.
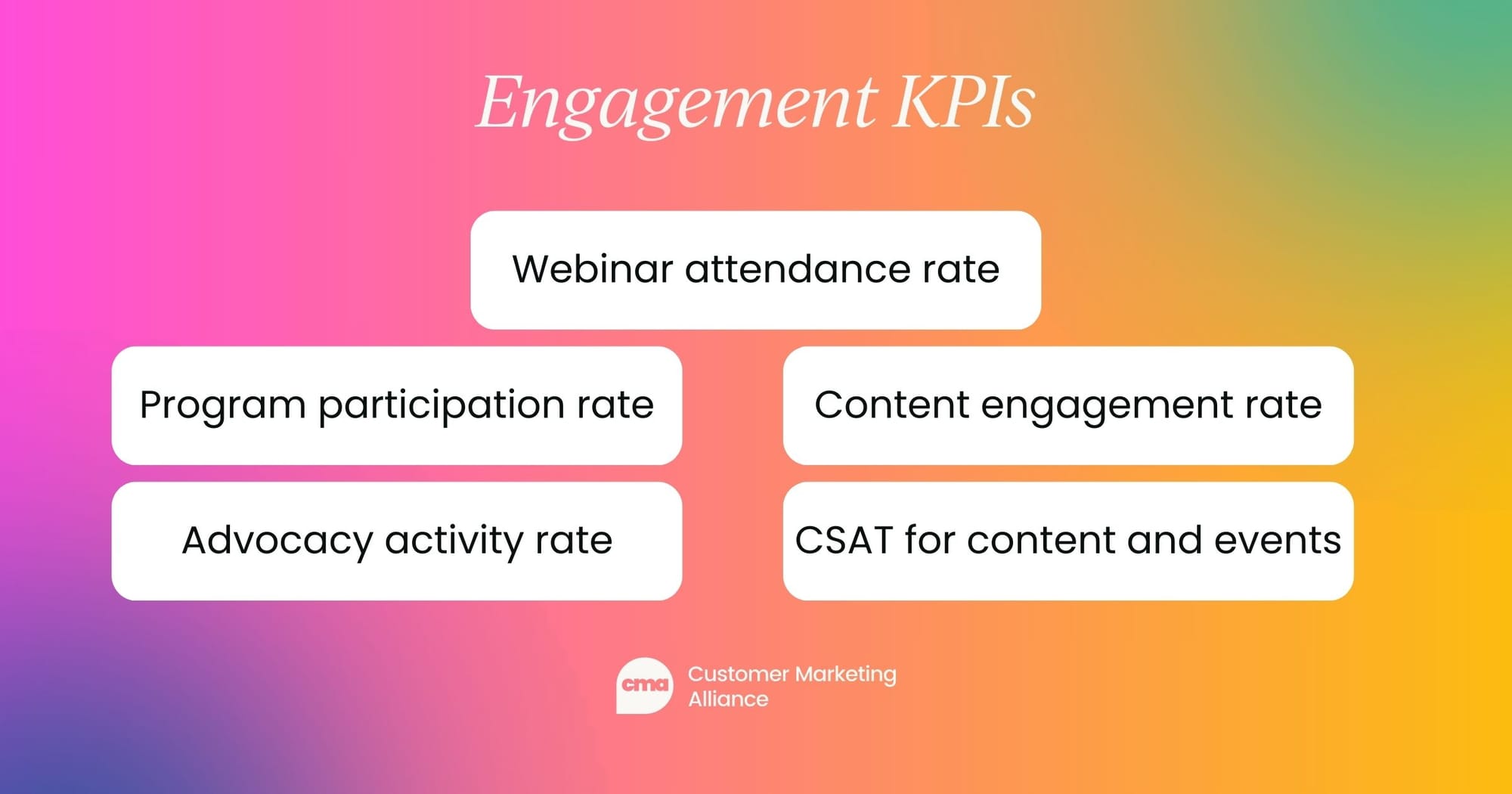
Engagement KPIs
You won't have revenue growth or advocacy without engaged customers. Measure how actively customers are participating in your programs and content by setting an engagement KPI:
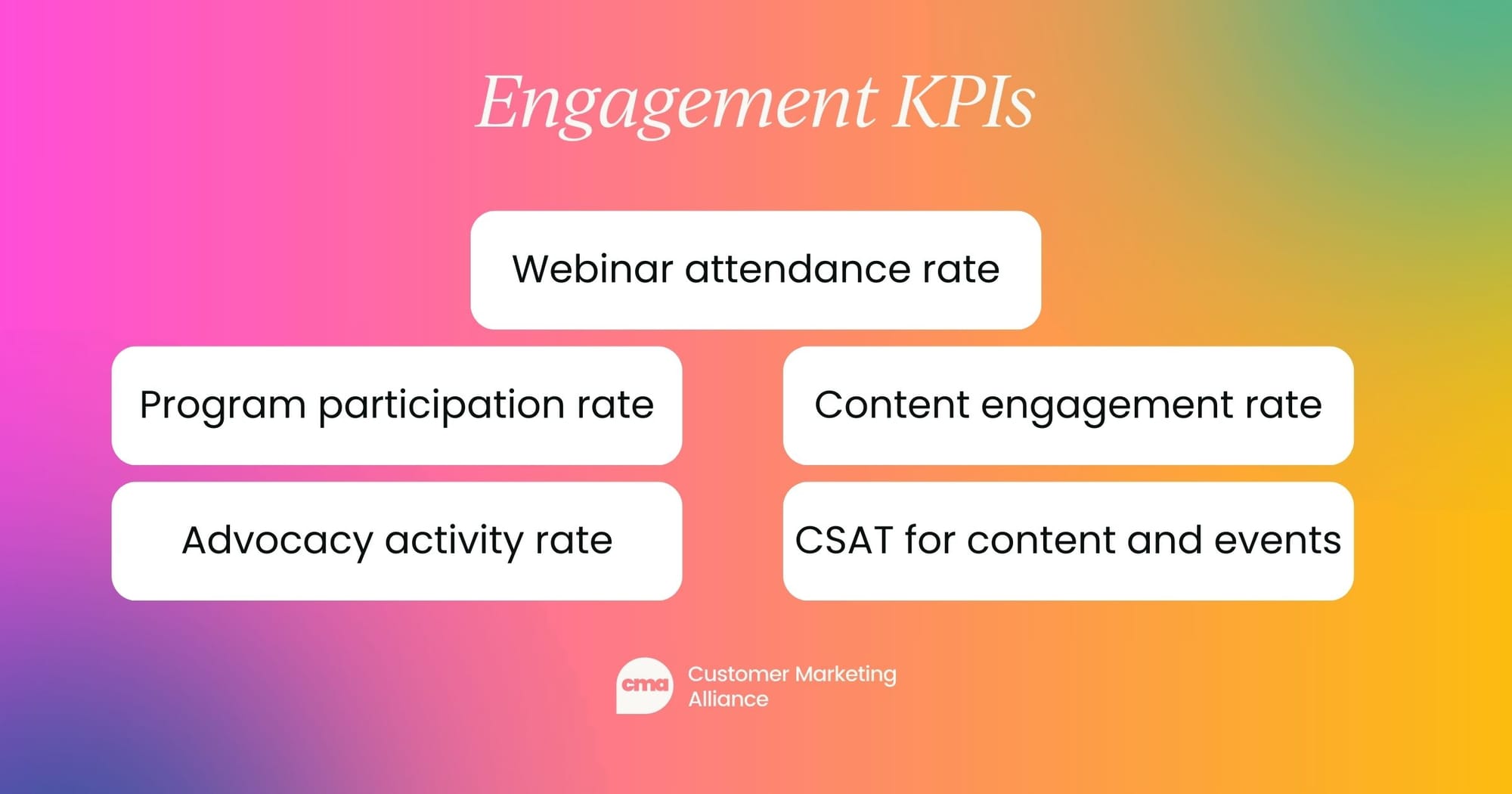
- Webinar attendance rate: Percentage of invited customers who attend webinars each month.
- Program participation rate: Percentage of customers actively engaging in loyalty or advocacy programs monthly.
- Content engagement rate: Percentage of content interactions (e.g., downloads, views, clicks) across campaigns.
- Advocate activity rate: Number of advocates participating in activities (e.g., beta tests, surveys) compared to total advocate base.
- CSAT for content and events: Average customer satisfaction score after events, webinars, or resource launches.
Growth and revenue KPIs
Increasing revenue is a significant responsibility in a customer marketer's role. Using growth and revenue as a KPI, you can track the direct business impact customer marketing strategies have on revenue generation.
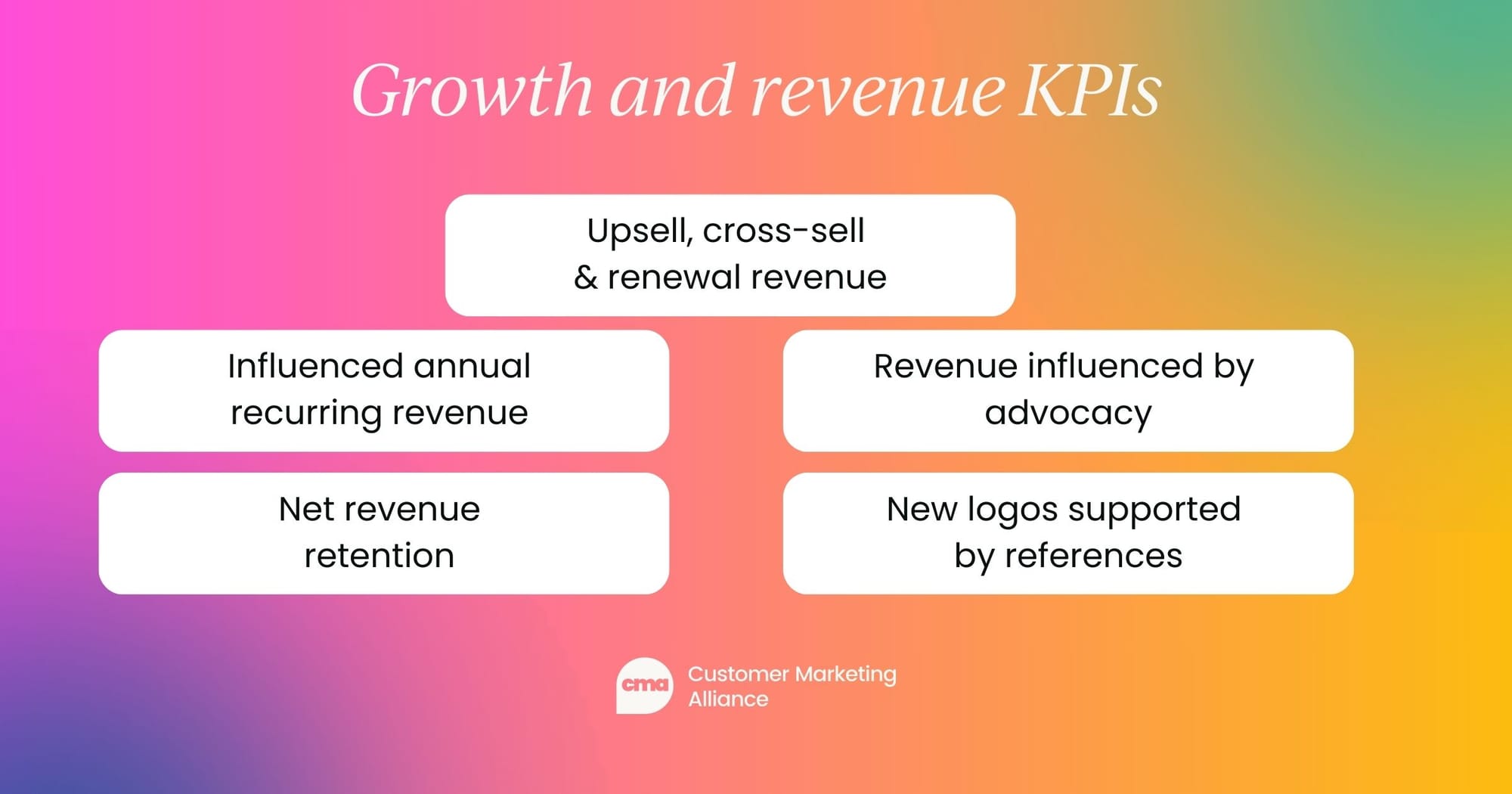
- Expansion revenue: Amount of revenue generated from upsells, cross-sells, and renewals each month.
- Influenced annual recurring revenue (ARR): Total revenue influenced by customer advocacy efforts, including references and testimonials.
- Net revenue retention (NRR): Percentage of retained revenue factoring in both churn and expansion revenue.
- Revenue influenced by advocacy: Total closed-won revenue directly connected to customer advocates or reference activity.
- New logos supported by references: Number of new deals closed with the help of customer references.
Retention and loyalty KPIs
Keeping tabs on how many customers you've retained is important to your overall business. By setting it as a KPI, you can measure how effectively your efforts are keeping customers engaged and loyal, all the while reducing churn.

- Churn rate: Percentage of customers who stop doing business with you within a month.
- Customer retention rate: Percentage of customers retained from the beginning to the end of the month.
- Net promoter score (NPS): Monthly average score from customer surveys measuring likelihood to recommend.
- Repeat purchase rate: Percentage of customers making repeat purchases or renewing subscriptions monthly.
- Time since last customer interaction: Average time since a customer last engaged with a campaign or event.
Customer education KPIs
Evaluate how well educational resources are driving product understanding and reducing support reliance.
- Training completions: Number of customers completing product training or certification programs monthly.
- Self-service help center usage: Number of visits and article views within the help center each month.
- Support ticket reduction: Percentage decrease in support tickets after the release of new educational materials.
- Content consumption rates: Percentage of customers engaging with onboarding guides, webinars, or tutorials monthly.
- Time-to-certification completion: Average time taken for customers to complete a training certification program.
Are customer marketing teams achieving their KPIs?
According to the State of Customer Marketing 2024 Report, when asked, "How well do you rate your team’s ability to meet KPIs?", customer marketing teams rated their success an average of 7.3 out of 10. The most frequently reported scores were 8, chosen by 28.7% of respondents, and 7, selected by 22.7%.
Here’s the full breakdown:
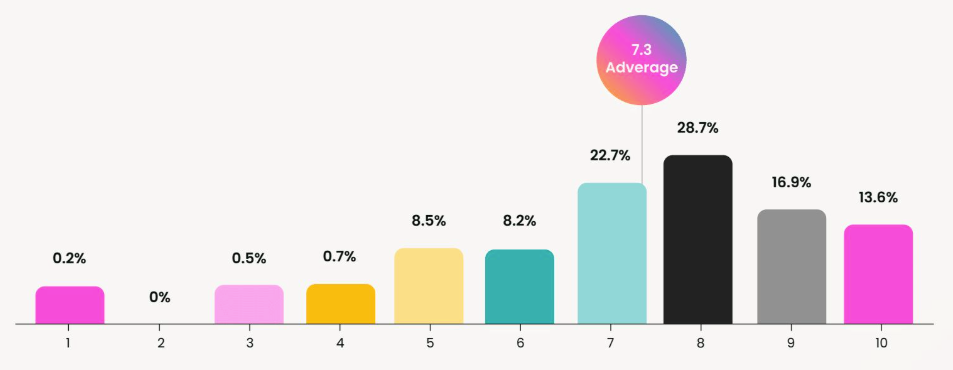
These findings have remained consistent over the past few years, with the majority of customer marketers describing their teams as "somewhat successful" in reaching KPI goals.
In 2023, for example, 65.2% identified as somewhat successful, while 11.6% felt neutral. The concentration of ratings around 7 and 8 indicates increasing confidence among customer marketing teams in their ability to meet performance targets.
Real-life KPI insights from top customer marketers
But what do customer marketing leaders make of the current state of KPIs?
Crystal Anderson, Director of Customer Marketing at SheerID, emphasizes the importance of KPI flexibility:
“Depending on your business goals, the most important KPI will change. I focus on three KPI pillars: engagement, activity, and growth. Under each, there are key metrics I monitor, with growth metrics often being the most crucial for proving business impact.”
Similarly, Vera Barile, Senior Customer Marketing Manager at AppDirect, highlights the importance of KPI specificity:
“KPIs need to be specific to the goal. What does the metric measure? Customer satisfaction? Retention? The number of references? CSAT, webinar registrations, and case study analytics all play a role in how success is defined.”

What is the difference between OKRs and KPIs?
OKRs and KPIs tend to be easily confused. While both are important for measuring progress and success, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
In fact, their purposes are such that they can work to complement each other when both are put into practice together.
OKRs are...
Focused:
OKRs are more qualitative in origin and prioritize the act of goal setting. They’ll describe what you want to accomplish, but your chosen key results can include a quantitative benchmark to aim for as a way of measuring success.
Flexible:
OKRs are typically given a specific time frame but are set up in such a way as to allow you to adjust these aims depending on your circumstances. Not reaching a specific OKR can tell you just as much about your current work as achieving it.
An ambitious goal can eke out the most important pain points in their first iteration, and can then be adjusted to focus on eliminating these pain points on the second go around.
Aligned:
OKRs are designed to align teams and individuals with the organization's overarching goals. Everyone's OKRs should weave into one another, and all exist to further the progress of achieving your company-wide goals.

KPIs are...
Specific:
KPIs are performance metrics used to measure specific parts of your work performance, often delving into the finer details rather than representing an "umbrella goal" for your team. They’re quantitative whereas OKRs are qualitative. They’ll be used to monitor ongoing activities and strategies, such as revenue, customer retention, upselling, or acts of advocacy.
Stable:
Where OKRs are flexible and prone to change and adjustments, KPIs are typically stable and remain the same throughout their use. Rather than being reviewed every quarter, or annually, KPIs should be regularly monitored, as often as week to week if needed, to ensure targets are met.
Isolated:
KPIs aren’t necessarily tied to specific objectives. While they can support broader goals, they do not provide the same level of high-level alignment as OKRs.
How do they work together?
In essence, KPIs are used continuously to help teams and leaders stay informed about the developing success of day-to-day work practices. OKRs can be brought in to improve a specific area of work over a set period of time.
If a KPI has dropped over the month, an OKR may be introduced to help direct the work in a way that supports and improves this KPI again.
| Aspect | OKRs | KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Drive strategic change | Track ongoing performance |
| Focus | Ambitious goals | Performance health |
| Timeframe | Fixed (quarterly or annually) | Continuous tracking |
| Measurement | Outcomes | Metrics |
It’s the intention behind setting these goals that’s most important, and then how you use them going forward.
Felipe Castro, a bonafide OKR-obsessor, has a brilliant analogy to help understand the difference:
“If you’re going on a trip to somewhere you’ve never been before, you’ll need a map and navigation system to show you how to get there, and a working car to get you there without any trouble.”
If your business is the car then:
- OKRs are the navigation system, and
- KPIs are the dashboard that monitors everything else going right with the car.
How to set effective OKRs and KPIs for your customer marketing team
Great OKRs strike a balance between ambition and clarity. Here’s how to create OKRs that work:
- Clear: Keep objectives simple and direct.
- Measurable: Use specific numbers to track progress.
- Time-bound: Set deadlines for achieving results.
- Challenging but achievable: Push yourself without setting unrealistic expectations.
When creating your KPIs, you want to ensure they align with your OKRs; otherwise, your overall ambition KPIs can be measured using the SMART framework:
🧠 S - Is your objective specific?
🧠 M - How will you measure your progress?
🧠 A - Is the goal realistically attainable?
🧠 R - How is the goal relevant to your organization?
🧠 T - What is the timeframe to achieve this goal?
It’s important to remember that KPIs are intended to be attainable, and are usually the product of an existing system or process. They’re also best when they use quantitative metrics for success and have a numbered goal.
You want to be careful that you monitor your KPIs closely, as they can fall by the wayside or become so convoluted that it’s impossible to know what path to take with them. When neglected, you may find your original intention is lost without up-to-date key milestones to keep you in check.

Best practices for OKR and KPI reporting
So, you’ve set your customer marketing OKRs? Nice one! Now it’s time to track, measure, and (most importantly) share the results.
It's all well and good creating your bespoke OKRs and KPIs, but without proper tracking and communication, even the best-laid plans can fall flat. Don’t worry, this part doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Keeping it simple and consistent is key.
Here are some tips for ensuring your reporting drives action and engagement:
- Create a dashboard: Use a central space to track both OKRs and KPIs.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overwhelming reports – focus on key insights.
- Update regularly: Share results frequently to keep momentum.
- Celebrate wins: Acknowledge progress, even small victories.
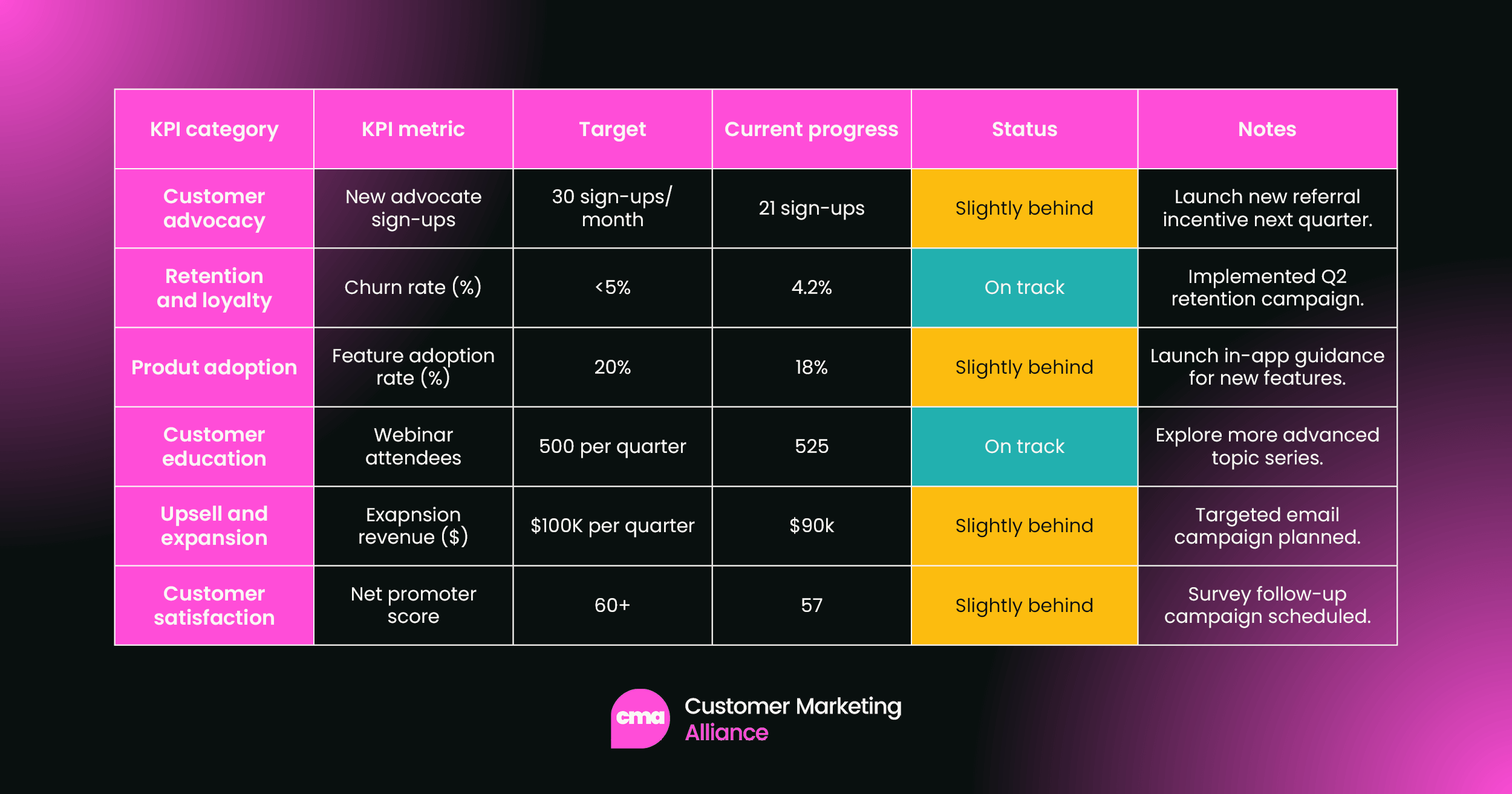
Example KPI reporting table
What have you learned?
OKRs and KPIs can be game-changers for customer marketing if used thoughtfully. They help you focus on what truly matters – keeping customers happy and loyal while proving your impact on the business.
Remember:
- Use OKRs for setting big-picture goals.
- Use KPIs for tracking everyday progress.
- Stay focused on metrics that truly reflect customer success.
Get these right, and you’ll not only hit your goals but also build deeper, lasting relationships with your customers that fuel long-term growth.
Where do you go from here?
So, you’ve read about what customer marketing is and why it is important and you’re now looking to understand what goes into actually implementing it into your existing network.
We've got just the thing for you – Customer Marketing Certified: Core.
- 12 modules
- 40+ chapters
- 10+ hours
- Templates and frameworks
- 6 fireside chats
- 100% self-paced
Customer Marketing Certified: Core is the industry standard, the driving force for your success, and the only companion you need for personal and professional growth.


 16 min read
16 min read
 Follow us on LinkedIn
Follow us on LinkedIn









